It also lets you compare projects with different time horizons and cash flow projections. Net present value (NPV) compares the value of future cash current ratio formula flows to the initial cost of investment. This allows businesses and investors to determine whether a project or investment will be profitable.
Calculating Net Present Value
Suppose your company is considering a project that will cost $30,000 this year. The cash inflow from this project is expected to be $6,000 next year and $8,000 the following year. The cash inflow is expected to increase by $2,000 yearly, resulting in a cash inflow of $18,000 in year 7, the final year of the project. Use a financial calculator to calculate NPV to determine whether this is a good project for your company to undertake (see Table 16.5). In practice, NPV is widely used to determine the perceived profitability of a potential investment or project to help guide critical capital budgeting and allocation decisions.
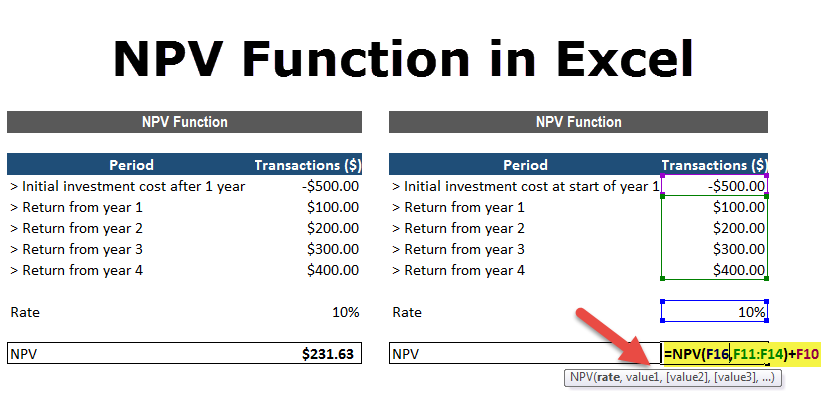
Calculating NVP
Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching. After almost a decade of experience in public accounting, he created MyAccountingCourse.com to help people learn accounting & finance, pass the CPA exam, and start their career. Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs.
Example 1: Even net cash flows
- This decision involves researching the company’s earnings reports, market position, and competitive advantages.
- Proposal X has the highest net present value but is not the most desirable investment.
- The cash inflow from this project is expected to be $6,000 next year and $8,000 the following year.
- Management is looking to expand into larger jobs but doesn’t have the equipment to do so.
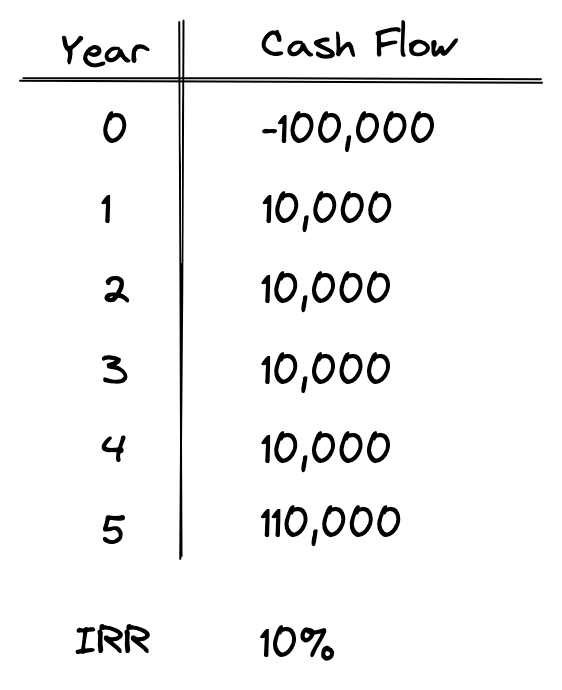
The final result is that the value of this investment is worth $61,446 today. It means a rational investor would be willing to pay up to $61,466 today to receive $10,000 every year over 10 years. By paying this price, the investor would receive an internal rate of return (IRR) of 10%.
Video Explanation of the NPV Formula
The profitability index is the ratio of the present value of cash inflows to the present value of cash outflows. A profitability index greater than one indicates a profitable investment or project. Investors use NPV to evaluate potential investment opportunities, such as stocks, bonds, or real estate, to determine which investments are likely to generate the highest returns. NPV is widely used in capital budgeting to evaluate the profitability of potential investments in long-term assets, such as machinery, equipment, and real estate.
NPV is widely used in capital budgeting and to know the profitability of the project. Imagine a company can invest in equipment that would cost $1 million and is expected to generate $25,000 a month in revenue for five years. Alternatively, the company could invest that money in securities with an expected annual return of 8%. Management views the equipment and securities as comparable investment risks.
Small changes in the discount rate can lead to large variations in NPV, making it challenging to determine the optimal investment or project. A negative NPV indicates that the investment or project is expected to result in a net loss in value, making it an unattractive opportunity. In this case, decision-makers should consider alternative investments or projects with higher NPVs. The internal rate of return (IRR) is the discount rate at which the net present value of an investment is equal to zero. Put another way, it is the compound annual return an investor expects to earn (or actually earned) over the life of an investment.
11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements. You could run a business, or buy something now and sell it later for more, or simply put the money in the bank to earn interest. Profitability is a key indicator of financial health and affects an organization’s ability to reinvest in growth, distribute dividends, or pay down debt. Investing in real estate involves purchasing physical properties (residential, commercial, or industrial) or investing through Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs). Connect to your warehouse, semantic layer, and hundreds of service APIs to put data analysis and dashboards into the hands of business users.
This concept is the foundation of NPV calculations, as it emphasizes the importance of considering the timing and magnitude of cash flows when evaluating investment opportunities. A young professional decides to contribute to a retirement account, such as a 401(k) or an IRA. This investment decision involves evaluating contribution limits, tax advantages, and investment options within the account. The individual considers their retirement goals and time horizon, deciding how much to invest regularly and which funds or assets to allocate within the retirement account to achieve growth over time. A conservative investor opts to purchase government bonds as part of a fixed-income strategy. This decision is made to secure a steady income stream with lower risk compared to stocks.
The investor also considers their risk tolerance and investment horizon, deciding whether to invest for short-term gains or long-term growth, thus reflecting a strategy based on personal financial goals. First, NPV calculations are based on assumptions about cash flows and discount rates. If these assumptions are accurate or change over time, the NPV calculation will be accurate. To construct an NPV profile for Sam’s, select several discount rates and compute the NPV for the embroidery machine project using each of those discount rates. Notice that if the discount rate is zero, the NPV is simply the sum of the cash flows. As the discount rate becomes larger, the NPV falls and eventually becomes negative.
